Difference between revisions of "Glossary"
From HighwayWiki
m |
m |
||
| (95 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This page is meant to define and clarify the meanings of traffic control terms and | + | [[File:Work_In_Progress.png]] |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This page is meant to define and clarify the meanings of traffic control terms and phrases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Words and Meanings= | ||
| − | == | + | ==<u>Signal Phasing Terms</u>== |
| − | <br> | + | |
| + | ===Four Way Independent Amber=== | ||
| + | :: An early signal color pattern in which the amber lamp illuminates during change from green to red (as in modern lights) as well as in red to green. Popular in the 1920's and 30's. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Flashing Yellow Arrow=== | ||
| + | [[File:McCain FYA traffic light.jpeg|thumb|Flashing Yellow Arrow traffic light in use in Huntsville, AL.]] | ||
| + | ::Many intersections contain doghouse signals to allow protected left turns. With leading left arrows, there's no harm. However, with lagging left arrows, the yellow trap becomes apparent. Pretend for a moment, you're approaching an intersection. There's 2 single face through signals, and a left turn doghouse over the left turn lane. There's already a car across from you waiting for a chance to make a left. All signals turn yellow, what do you think? You think the cycle is ending, so to prevent being stuck for longer than you need to, you try to beat the red and you make the left. Here's the problem: That yellow your side received isn't what the other side received. Your side got that yellow because the doghouses at that intersection are lagging, not leading. The car across from you waiting to turn triggered your side's cycle to end early, while the other side's through traffic still has green, right as you're cutting across the road. Bam! To fix this, engineers designed the Flashing Yellow Arrow, a signal configuration designed to prevent and eliminate yellow traps. Instead of leading drivers to make their own left turn judgments, it provides a flashing yellow arrow to signify left turns might not be safe, and the driver should yield when making left turns. A very useful webpage further explaining FYAs can be viewed [http://midimagic.sgc-hosting.com/leadlag.htm here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Interval=== | ||
| + | :: TBD | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| − | + | ===Leading / Lagging Arrow=== | |
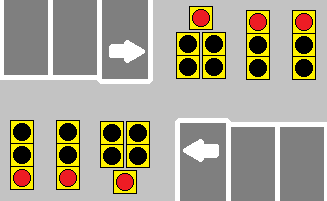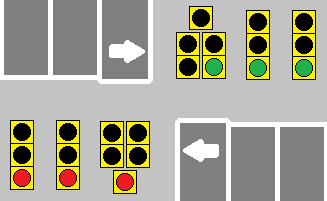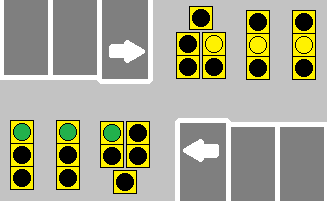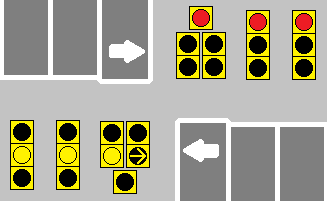
:: When a dedicated turn arrow is offered at a signal-controlled intersection, its operation will often be defined as either 'Leading' or 'Lagging'. Leading arrows happen at the beginning of the through green cycle, and generally end with a yellow arrow before the through green is finished. Lagging arrows often happen towards the end of the through green cycle, and usually have their yellow arrows tied with the through yellow, or simply rely on the through yellow entirely. | :: When a dedicated turn arrow is offered at a signal-controlled intersection, its operation will often be defined as either 'Leading' or 'Lagging'. Leading arrows happen at the beginning of the through green cycle, and generally end with a yellow arrow before the through green is finished. Lagging arrows often happen towards the end of the through green cycle, and usually have their yellow arrows tied with the through yellow, or simply rely on the through yellow entirely. | ||
:: Signals that work together at either end of a bridge or overpass often feature lagging arrows to help clear out the short span of road between the two intersections, to help prevent cars from getting stuck in line while trying to turn. | :: Signals that work together at either end of a bridge or overpass often feature lagging arrows to help clear out the short span of road between the two intersections, to help prevent cars from getting stuck in line while trying to turn. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | :: [[File:Leading-Lagging Arrow.gif]] | ||
| + | ::<b>The forward-facing signals demonstrate a leading arrow, whereas the reverse-facing signals demonstrate a lagging arrow.</b> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | ===Phase=== | |
| + | A phase is a single direction of traffic that cannot be services with other phases in the same ring. | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| − | :: | + | ===Split/Overlapping Amber=== |
| + | :: An early signal color pattern in which the amber lamp illuminates during the end of the green lamp cycle following which both lamps turn off and the red lamp illuminates. Popular in the 1920's and 30's. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==<u>Terms of Physical Signal Features</u>== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===#-Way Signal=== | ||
| + | :: A single signal assembly that has lights on # sides. These may also be referred to as 4-way signals with (4-#) blank sides. Other common trade names for them are square and box signals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Adjustable=== | ||
| + | :: Any signal, or correctly a signal cluster, in which the various faces can be set at differing angles from one another. Compare with nonadjustable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Aspect=== | ||
| + | :: The number of aspects a signal has is basically saying how many indications it has. A single aspect beacon has one indication, for example. | ||
| + | [[File:Dualaspectbeaconpyth.jpg|thumb|A dual-aspect bridge pillar beacon.]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bar Lens (Adler Lens)=== | ||
| + | :: A signal lens with a smooth glass "bar" through the center. Akin to some railroad signals, the bar is horizontal for red, diagonal for yellow, and vertical for green. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Blank Door=== | ||
| + | [[File:TSIBlankDoor.JPG |thumb|A blank door in use on a 3-way signal.]] | ||
| + | :: A door that was designed without any mountings for a visor or lens. These were used on nonadjustable signals where one side didn't face a street or faced against the flow of traffic on a one-way street. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Broad Arrow Lens=== | ||
| + | [[File:Broadarrow-tim.jpg|thumb|An 8" Kopp TL-4709, from the collection of BigTbird1974.]] | ||
| + | :: A non-standard arrow indication, the broad arrow features a complete triangle arrow head. Offered in both 8" and 12" sizes, and somewhat rarer than chinese arrow lenses. | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cast Visor=== | ||
| + | [[File:CastVisor.JPG|thumb|A cast visor on a Crouse-hinds DT signal.]] | ||
| + | :: Term referring to a signal that has the visor assembled as a nonremovable component of the body, housing, or door. These visors are generally much thicker than removable visors. Much more popular in the early days and porthole signals such as Darley and Crouse-Hinds through the Deco era. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Chinese Arrow Lens=== | ||
| + | [[File:Chinesearrows-tim.jpg|left|thumb|All 3 8" chinese lenses offered. From the collection of BigTbird1974.]] | ||
| + | :: A non-standard arrow indication. The cutout is much thicker, and the stem is tapered along with the arrowhead. Chinese arrows are generally seen in the 8" variety. 12" chinese arrows were made, but are very rare. | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cluster=== | ||
| + | [[File:Lfeclusterpyth.jpg|thumb|A cluster of 8" LFE Automatics.]] | ||
| + | :: Often mistakenly called 4-ways, a cluster is a pole or spanwire group of signals that are mounted together with common hardware fittings. By definition, clusters are adjustable signals. | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Command Lens=== | ||
| + | [[ File:Waitlenspyth.jpg |thumb|left|A 'WAIT' lens, used in early pedestrian signals.]] | ||
| + | :: A signal lens with a message embossed on the glass; typically STOP for the red lens, CAUTION for the yellow, and GO for the green lens. One common example of a special-purpose command lens is THANK YOU on a green tollbooth signal. | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
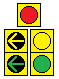
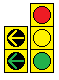
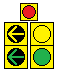
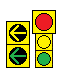
| + | ===Doghouse Signal=== | ||
| + | ::When MUTCD started requiring green arrows to be terminated with yellow arrows (instead of just going dark) on shared-face signals, many jurisdictions didn't have the vertical clearance required for a signal with 5 sections (R-Y-G-YA-GA) to be hung in a stack over traffic. To overcome this issue, the doghouse configuration came to be. This consists of a red section centered above two 2-section stacks: one of yellow & green arrows for the turning traffic, the other of yellow & green balls for the thru traffic A Left Doghouse has the arrow stack on the left, a Right Doghouse has the arrow stack on the right. This creates a doghouse shape if one were to loosely trace the configuration.<br> | ||
| + | ::[[File:Doghouse-l&r.png]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | ::Here are the most common terms for different size configurations of a typical doghouse signal:<br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | :: '''''"Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: All sections are 12"; red is centered | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse.png]] [[File:WinkomaticDoghouse.JPG |thumb|A doghouse signal.]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | :: '''''"Crooked Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: All sections are 12"; red is off center | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-Crooked.png]] [[File:Offsetdoghousepyth.jpg|thumb|An offset doghouse signal.]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | :: '''''"Pinhead Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: The Red is 8", all other sections are 12" | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouses-Pinhead.png]] | ||
| + | :: '''''"Franken-Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: The Red & Arrows are 12", the Green & Yellow are 8" | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-Mixed.png]] | ||
| + | :: '''''"Cheap Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: The R, Y, & G sections are 8", the Arrows are 12" | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-Cheap.png]] [[File:Cheapdoghousepyth.jpg|thumb|A cheap doghouse signal.]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | :: '''''"Delaware Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: The Red is 12", all other sections are 8" | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-Delaware.png]] | ||
| + | :: '''''"8-inch Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: All sections are 8" | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-8".png]] [[File:8indoghousepyth.jpg|thumb|8" doghouse.]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | ::Before the [[#Flashing Yellow Arrow|"Yellow Trap" signal]] came around, the flashing yellow arrow concept was introduced by doghouse signals [?]. These are much less common than the [[#Flashing Yellow Arrow|"Yellow Trap" signal]]s. Below are two versions of it.<br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | :: '''''"FYA Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: Functions the same as a [[#Flashing Yellow Arrow|"Yellow Trap" signal]], but with an extra clearance yellow. | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-FYA.gif]] | ||
| + | :: '''''"Bimodal FYA Doghouse"''''' | ||
| + | :: Functions the same as a normal doghouse, with an extra yellow arrow that flashes with the green ball whenever the green arrow isn't lit. | ||
| + | :: [[File:Doghouse-BFYA.gif]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Door=== | ||
| + | :: The part of a signal that holds the lens and visor. It's typically used to access the inside of the signal to change the bulb or LED module in the signal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Face=== | ||
| + | :: The face of the signal is the side seen most often, featuring the indications and visors. While single-face signals have the housing on the other sides of the body, 4-way signals have 4 faces. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Franken-Signal=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::When a traffic signal (whether in public or not) is composed of sections or parts from multiple manufacturers or models from the same manufacturer that aren't designed to normally go together, this signal is unofficially called a Franken-Signal, in reference to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frankenstein Frankenstein's Monster]. Due to newer signal models being composed of individual indication sections, contractors sometimes do this in the field to help use up old sections laying around and to save money. The term Franken-Signal generally only applies to the housings; lenses are often more difficult to spot as incorrect from ground level and often don't make enough of a difference to be discernible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Louver=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Louvers Undershot.jpeg|thumb|Undershot of some louvers in use in Huntsville, AL.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::A louver is a round metal frame with vertical or horizontal slats that is placed in the signal's visor(s) to limit visibility of the respective indication. Often thought of as the poor man's PV signal, it basically does the same thing, although louvers are limited to either vertical or horizontal view limiting at a given time, whereas a PV signal can limit specific spots and zones. Louvers exist with different slat amounts, presumably to offer different intensities of view limitation. Louvers are usually, but not always, placed in tunnel or full circle visors. Louvers are popular places for birds to create nests. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Nonadjustable=== | ||
| + | :: Describes any signal, such as a 4-way, in which the body or signal assembly has fixed angles, typically 90deg, between the various viewing faces. Compare with adjustable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Porthole=== | ||
| + | :: General descriptive term referring to several early styles of signals. These signals did not have a conventional rectangular/square door that opened to allow bulb and interior access; instead, the door was a minimial ring containing the lens and visor resembling the porthole window style on ships. In the case of Tokheim, Harrington-Seaberg, Autoflow and a few others these portholes were hinged to the body while signals such as Crouse-Hinds and W. S. Darley had hingeless doors that were removed from the signal for servicing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Programmed Visibility=== | ||
| + | :: A signal that is designed to project an indication to a specific lane of traffic only. This is accomplished by using a special diffractive lens that filters the light waves in one direction. Most programmed visibility signals in the USA are made by the 3M Company. Such signals are employed in intersections with potentially ambiguous geometry, or for left-turn only signal faces that are likely to be misread by straight-thru traffic. They may also be used to prevent confusion when one signal quickly succeeds another. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :: See also: [[3M#Programmable_Visibility_Signals|3M]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sectional=== | ||
| + | :: Loosely termed as a way to describe a signal in which the various lense sections (IE Red, Yellow, Green) are physically seperate and not cast as a solid piece of metal. Both modern signals and the rodded style signals fall under this definition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Section==== | ||
| + | :: Like Sectional, section refers to one housing, lens, visor, etc. assembly of a signal. A stoplight or caution flasher can be a signal of only one section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Symbolic Pedestrian Signal=== | ||
| + | :: A pedestrian signal that uses symbols instead of words on the lens(es). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Hand-Man Pedestrian Signal==== | ||
| + | :: A pedestrian signal that uses a raised hand for the stop indication and a man walking for the walk indication. These are the most common pedestrian signals in the US & Canada. [[File:DurasigPeds.JPG |thumb|Hand/Man Durasig pedestrian signals. The man indication can be seen, despite it being off.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Visor=== | ||
| + | :: The hood, flange, or shield that is used to provide a tunnel effect around a lens. Common styles are the western Full Circle, exactly as its name suggests; the Tunnel (or Combination), a circle with no bottom, and the Cutaway or Cap, which is a tunnel with the sides also removed. These are typically from 7-10" long with various downward angles. Many special purpose variations exist. Angled visors are extended length full circle visors with an angled, instead of flush cut at the end to restrict the viewing angle and are produced in directional specific (right, left) variants. Tunnaways are a nickname given to older Marbelite signal visors due to their unique shape - while they were scalloped like a cutaway visor, the cut was made much closer to the front of the signal than a typical cutaway giving ti a tunnel visor appearance. A rarer version of the Tunnaway was made by Crouse-Hinds, where one side of the visor was a typical CH cap pattern, but the other side had a full tunnel shape to it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Worded Pedestrian Signal=== | ||
| + | :: A pedestrian signal that uses words instead of symbols on the lens(es). The MUTCD outlawed these on new installations in 2003. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====WAIT-WALK Pedestrian Signal==== | ||
| + | :: A pedestrian signal that has the words "Wait" and "Walk" on the two lenses. These are very hard to find in service today. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Walk-Don't Walk Pedestrian Signal==== | ||
| + | :: A pedestrian signal that has "Don't Walk" on one lens and "Walk" on the other. [[File:9inchAlusigPed.JPG |thumb|Alusig pedestrian signal showing both the Walk and Don't Walk indications at the same time.]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 00:32, 13 July 2016
This page is meant to define and clarify the meanings of traffic control terms and phrases.
Contents
- 1 Words and Meanings
- 1.1 Signal Phasing Terms
- 1.2 Terms of Physical Signal Features
- 1.2.1 #-Way Signal
- 1.2.2 Adjustable
- 1.2.3 Aspect
- 1.2.4 Bar Lens (Adler Lens)
- 1.2.5 Blank Door
- 1.2.6 Broad Arrow Lens
- 1.2.7 Cast Visor
- 1.2.8 Chinese Arrow Lens
- 1.2.9 Cluster
- 1.2.10 Command Lens
- 1.2.11 Doghouse Signal
- 1.2.12 Door
- 1.2.13 Face
- 1.2.14 Franken-Signal
- 1.2.15 Louver
- 1.2.16 Nonadjustable
- 1.2.17 Porthole
- 1.2.18 Programmed Visibility
- 1.2.19 Sectional
- 1.2.20 Symbolic Pedestrian Signal
- 1.2.21 Visor
- 1.2.22 Worded Pedestrian Signal
Words and Meanings
Signal Phasing Terms
Four Way Independent Amber
- An early signal color pattern in which the amber lamp illuminates during change from green to red (as in modern lights) as well as in red to green. Popular in the 1920's and 30's.
Flashing Yellow Arrow
- Many intersections contain doghouse signals to allow protected left turns. With leading left arrows, there's no harm. However, with lagging left arrows, the yellow trap becomes apparent. Pretend for a moment, you're approaching an intersection. There's 2 single face through signals, and a left turn doghouse over the left turn lane. There's already a car across from you waiting for a chance to make a left. All signals turn yellow, what do you think? You think the cycle is ending, so to prevent being stuck for longer than you need to, you try to beat the red and you make the left. Here's the problem: That yellow your side received isn't what the other side received. Your side got that yellow because the doghouses at that intersection are lagging, not leading. The car across from you waiting to turn triggered your side's cycle to end early, while the other side's through traffic still has green, right as you're cutting across the road. Bam! To fix this, engineers designed the Flashing Yellow Arrow, a signal configuration designed to prevent and eliminate yellow traps. Instead of leading drivers to make their own left turn judgments, it provides a flashing yellow arrow to signify left turns might not be safe, and the driver should yield when making left turns. A very useful webpage further explaining FYAs can be viewed here.
Interval
- TBD
Leading / Lagging Arrow
- When a dedicated turn arrow is offered at a signal-controlled intersection, its operation will often be defined as either 'Leading' or 'Lagging'. Leading arrows happen at the beginning of the through green cycle, and generally end with a yellow arrow before the through green is finished. Lagging arrows often happen towards the end of the through green cycle, and usually have their yellow arrows tied with the through yellow, or simply rely on the through yellow entirely.
- Signals that work together at either end of a bridge or overpass often feature lagging arrows to help clear out the short span of road between the two intersections, to help prevent cars from getting stuck in line while trying to turn.
Phase
A phase is a single direction of traffic that cannot be services with other phases in the same ring.
Split/Overlapping Amber
- An early signal color pattern in which the amber lamp illuminates during the end of the green lamp cycle following which both lamps turn off and the red lamp illuminates. Popular in the 1920's and 30's.
Terms of Physical Signal Features
#-Way Signal
- A single signal assembly that has lights on # sides. These may also be referred to as 4-way signals with (4-#) blank sides. Other common trade names for them are square and box signals.
Adjustable
- Any signal, or correctly a signal cluster, in which the various faces can be set at differing angles from one another. Compare with nonadjustable.
Aspect
- The number of aspects a signal has is basically saying how many indications it has. A single aspect beacon has one indication, for example.
Bar Lens (Adler Lens)
- A signal lens with a smooth glass "bar" through the center. Akin to some railroad signals, the bar is horizontal for red, diagonal for yellow, and vertical for green.
Blank Door
- A door that was designed without any mountings for a visor or lens. These were used on nonadjustable signals where one side didn't face a street or faced against the flow of traffic on a one-way street.
Broad Arrow Lens
- A non-standard arrow indication, the broad arrow features a complete triangle arrow head. Offered in both 8" and 12" sizes, and somewhat rarer than chinese arrow lenses.
Cast Visor
- Term referring to a signal that has the visor assembled as a nonremovable component of the body, housing, or door. These visors are generally much thicker than removable visors. Much more popular in the early days and porthole signals such as Darley and Crouse-Hinds through the Deco era.
Chinese Arrow Lens
- A non-standard arrow indication. The cutout is much thicker, and the stem is tapered along with the arrowhead. Chinese arrows are generally seen in the 8" variety. 12" chinese arrows were made, but are very rare.
Cluster
- Often mistakenly called 4-ways, a cluster is a pole or spanwire group of signals that are mounted together with common hardware fittings. By definition, clusters are adjustable signals.
Command Lens
- A signal lens with a message embossed on the glass; typically STOP for the red lens, CAUTION for the yellow, and GO for the green lens. One common example of a special-purpose command lens is THANK YOU on a green tollbooth signal.
Doghouse Signal
- When MUTCD started requiring green arrows to be terminated with yellow arrows (instead of just going dark) on shared-face signals, many jurisdictions didn't have the vertical clearance required for a signal with 5 sections (R-Y-G-YA-GA) to be hung in a stack over traffic. To overcome this issue, the doghouse configuration came to be. This consists of a red section centered above two 2-section stacks: one of yellow & green arrows for the turning traffic, the other of yellow & green balls for the thru traffic A Left Doghouse has the arrow stack on the left, a Right Doghouse has the arrow stack on the right. This creates a doghouse shape if one were to loosely trace the configuration.
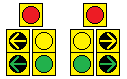
- When MUTCD started requiring green arrows to be terminated with yellow arrows (instead of just going dark) on shared-face signals, many jurisdictions didn't have the vertical clearance required for a signal with 5 sections (R-Y-G-YA-GA) to be hung in a stack over traffic. To overcome this issue, the doghouse configuration came to be. This consists of a red section centered above two 2-section stacks: one of yellow & green arrows for the turning traffic, the other of yellow & green balls for the thru traffic A Left Doghouse has the arrow stack on the left, a Right Doghouse has the arrow stack on the right. This creates a doghouse shape if one were to loosely trace the configuration.
- Here are the most common terms for different size configurations of a typical doghouse signal:
- Here are the most common terms for different size configurations of a typical doghouse signal:
- Before the "Yellow Trap" signal came around, the flashing yellow arrow concept was introduced by doghouse signals [?]. These are much less common than the "Yellow Trap" signals. Below are two versions of it.
- Before the "Yellow Trap" signal came around, the flashing yellow arrow concept was introduced by doghouse signals [?]. These are much less common than the "Yellow Trap" signals. Below are two versions of it.
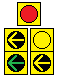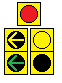
- "FYA Doghouse"
- Functions the same as a "Yellow Trap" signal, but with an extra clearance yellow.
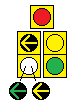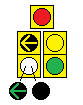
- "Bimodal FYA Doghouse"
- Functions the same as a normal doghouse, with an extra yellow arrow that flashes with the green ball whenever the green arrow isn't lit.
Door
- The part of a signal that holds the lens and visor. It's typically used to access the inside of the signal to change the bulb or LED module in the signal.
Face
- The face of the signal is the side seen most often, featuring the indications and visors. While single-face signals have the housing on the other sides of the body, 4-way signals have 4 faces.
Franken-Signal
- When a traffic signal (whether in public or not) is composed of sections or parts from multiple manufacturers or models from the same manufacturer that aren't designed to normally go together, this signal is unofficially called a Franken-Signal, in reference to Frankenstein's Monster. Due to newer signal models being composed of individual indication sections, contractors sometimes do this in the field to help use up old sections laying around and to save money. The term Franken-Signal generally only applies to the housings; lenses are often more difficult to spot as incorrect from ground level and often don't make enough of a difference to be discernible.
Louver
- A louver is a round metal frame with vertical or horizontal slats that is placed in the signal's visor(s) to limit visibility of the respective indication. Often thought of as the poor man's PV signal, it basically does the same thing, although louvers are limited to either vertical or horizontal view limiting at a given time, whereas a PV signal can limit specific spots and zones. Louvers exist with different slat amounts, presumably to offer different intensities of view limitation. Louvers are usually, but not always, placed in tunnel or full circle visors. Louvers are popular places for birds to create nests.
Nonadjustable
- Describes any signal, such as a 4-way, in which the body or signal assembly has fixed angles, typically 90deg, between the various viewing faces. Compare with adjustable.
Porthole
- General descriptive term referring to several early styles of signals. These signals did not have a conventional rectangular/square door that opened to allow bulb and interior access; instead, the door was a minimial ring containing the lens and visor resembling the porthole window style on ships. In the case of Tokheim, Harrington-Seaberg, Autoflow and a few others these portholes were hinged to the body while signals such as Crouse-Hinds and W. S. Darley had hingeless doors that were removed from the signal for servicing.
Programmed Visibility
- A signal that is designed to project an indication to a specific lane of traffic only. This is accomplished by using a special diffractive lens that filters the light waves in one direction. Most programmed visibility signals in the USA are made by the 3M Company. Such signals are employed in intersections with potentially ambiguous geometry, or for left-turn only signal faces that are likely to be misread by straight-thru traffic. They may also be used to prevent confusion when one signal quickly succeeds another.
- See also: 3M
Sectional
- Loosely termed as a way to describe a signal in which the various lense sections (IE Red, Yellow, Green) are physically seperate and not cast as a solid piece of metal. Both modern signals and the rodded style signals fall under this definition.
Section
- Like Sectional, section refers to one housing, lens, visor, etc. assembly of a signal. A stoplight or caution flasher can be a signal of only one section.
Symbolic Pedestrian Signal
- A pedestrian signal that uses symbols instead of words on the lens(es).
Hand-Man Pedestrian Signal
- A pedestrian signal that uses a raised hand for the stop indication and a man walking for the walk indication. These are the most common pedestrian signals in the US & Canada.
Visor
- The hood, flange, or shield that is used to provide a tunnel effect around a lens. Common styles are the western Full Circle, exactly as its name suggests; the Tunnel (or Combination), a circle with no bottom, and the Cutaway or Cap, which is a tunnel with the sides also removed. These are typically from 7-10" long with various downward angles. Many special purpose variations exist. Angled visors are extended length full circle visors with an angled, instead of flush cut at the end to restrict the viewing angle and are produced in directional specific (right, left) variants. Tunnaways are a nickname given to older Marbelite signal visors due to their unique shape - while they were scalloped like a cutaway visor, the cut was made much closer to the front of the signal than a typical cutaway giving ti a tunnel visor appearance. A rarer version of the Tunnaway was made by Crouse-Hinds, where one side of the visor was a typical CH cap pattern, but the other side had a full tunnel shape to it.
Worded Pedestrian Signal
- A pedestrian signal that uses words instead of symbols on the lens(es). The MUTCD outlawed these on new installations in 2003.
WAIT-WALK Pedestrian Signal
- A pedestrian signal that has the words "Wait" and "Walk" on the two lenses. These are very hard to find in service today.
Walk-Don't Walk Pedestrian Signal
- A pedestrian signal that has "Don't Walk" on one lens and "Walk" on the other.